|
 |
Dynamics |
| |
 |
4-3: Change in velocity - the airways as roads |
 |
4-8: Quasi-static vs. high flow lung expansion |
 |
4-9: Small airways and the tethering effect of the lung |
 |
4-10A: Equal pressure point |
 |
4-10B: Starling resistor |
 |
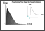
4-12A: Flow-volume plot |
 |
4-12B: 3D flow-volume-time graph for forced exhalation |
 |
4-13: Flow limitation and the equal pressure point |
 |
4-15: Location of the equal pressure point |
|
|
|